The salt-bath furnace is important heating equipment in the metal heat treatment process with simple structure, convenient use and maintenance, and low investment and maintenance costs. Sometimes, it can also be used in welding processes. The graphite electrode is the core component of the salt-bath furnace. In order to overcome the shortcomings of short electrode life, we have studied a new type of “graphite composite electrode” through exploration and practice. Its life is about 10 times that of traditional steel electrodes.

Comparison of Two Types of the Graphite Electrode Structure
The electrode is the core component of the salt-bath furnace. When developing the graphite electrodes, it mainly focuses on the shape of the furnace, the electrode layout, and the type of the salt-bath furnace. In the specific design of the electrode, factors such as simple structure, easy manufacture, low cost, and convenient installation and maintenance must also be considered.
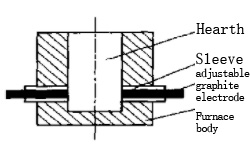
Structure of adjustable graphite electrode
The furnace body is the same as the general salt-bath furnace, and the graphite electrode structure is special, and the electrode needs to be designed in an adjustable form. As shown in Figure 1. The sleeve material is graphite, which is equivalent to a large square nut, which is embedded and fixed in the furnace body on the left and right sides (symmetrical positions). The adjustable electrode material is graphite, which is equivalent to a large screw. Screw-in the sleeve during installation and threaded connection. The exposed end has a square (or hexagonal) head, which is convenient to use a wrench to move the electrode so that the electrode can rotate freely in the sleeve. During the use of the furnace, due to the corrosion and dissolution loss of the molten salt to the electrode, the electrode can be adjusted and compensated, but the dissolution loss of the sleeve cannot be compensated.
The combined electrode is divided into two parts: graphite and steel. The graphite part is in contact with molten salt, one end of the steel part is exposed to contact with the air, although the other end is buried in the furnace. Since the graphite electrode isolates the molten salt and does not directly contact the molten salt, the current flows through the line from the steel electrode to the graphite electrode and then to the molten salt. After the electrodes are assembled, they are inserted into the hearth from the back of the hearth, distributed on both sides of the hearth, 65mm from the bottom of the hearth. The whole set of electrodes is of a plate-shaped structure for cooling and sealing with water, which is not only easy to assemble, but also simple in structure, easy to process, easy to assemble and disassemble, and low in cost. Its layout is also completely different from the adjustable graphite electrode. Figure 2 is a layout diagram of a single-phase 45kW side-embedded graphite composite electrode. On the basis of analysis and research on adjustable graphite electrodes, in order to solve the problems of adjustable graphite electrodes, a new type of graphite composite electrode was developed.
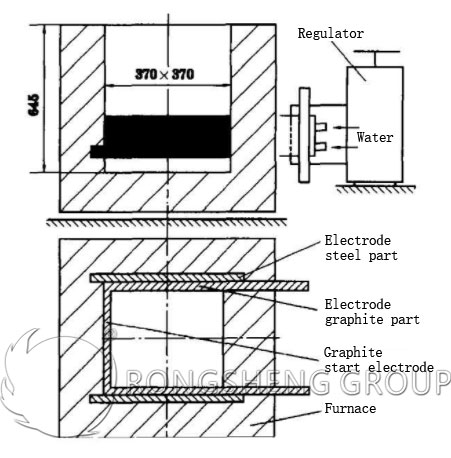
New type Graphite Composite Electrode
The auxiliary electrode of the salt-bath furnace is specially designed for the start-up of the salt-bath furnace because the start-up of the salt-bath furnace has always been one of the urgent problems to be solved. There have been many innovative attempts in the past ten years, but not many are currently used in the production site. Most of the sites still use traditional spiral steel starting electrodes, which have a long starting time, high energy consumption, and inconvenient operation. In addition, the dissolution of the steel starting electrode increases the oxides in the molten salt, which adversely affects the heating quality of the workpiece. The advent of graphite composite electrodes provides a new way to promote the development of start-up technology.
The basis for designing the graphite starter electrode is that the resistance of molten salt is very high in the solid state at room temperature, and the resistance is very small after being melted into a liquid state, and the speed of change is fast. The resistance of graphite materials decreases slowly with increasing temperature. Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the resistance of molten salt and graphite as a function of temperature. N is the intersection of the two curves, that is when the temperature is NT, the molten salt and the starting graphite electrode have the same resistance NΩ.
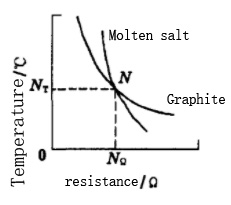
Under our test conditions, the measured NT is about 610~620℃. At this temperature, the macroscopic state is: the molten salt has begun to melt, and part of the current begins to flow through the liquid molten salt. The graphite starter electrode is still energized, but the current is weakened. As time goes by, the melting area of the molten salt continues to expand, and the resistance of the molten salt is further reduced due to the increase in the volume of the conductive liquid molten salt. Therefore, the current flowing through the liquid molten salt is also increasing, while the current flowing through the graphite starting electrode gradually decreases. As the temperature rises, when the resistance of the liquid molten salt is much smaller than the resistance of the starting electrode, most of the current flows to the liquid molten salt through the graphite main electrode, and the starting process is basically completed. When designing, convert the value of NΩ to the resistance value of the graphite starting electrode at room temperature. The resistance value depends on the resistivity of the material of the starting electrode and the geometric size of the design. The geometric size is related to factors such as the shape of the furnace, the distance between the two main electrodes, the composition, and the ratio of the molten salt raw materials.
Advantages of Combined Graphite Electrode
The graphite composite electrode is successfully developed after a long period of practice and exploration on the basis of overcoming the problems existing in the adjustable graphite electrode. The outstanding feature of the graphite composite electrode is that it solves the oxidation of the exposed end of the graphite electrode, the connection between the graphite electrode and the copper plate of the power supply is difficult, the furnace temperature is not uniform, the electrode dissolves quickly and the life is not long. The graphite composite electrode is designed into a plate shape, which makes the electrode easy to process and easy to assemble. Common graphite materials are selected, which realize low cost and are convenient for popularization and application. The manufacture of graphite starter electrodes opens up a new way of starter technology. The production of graphite composite electrodes reduces harmful impurities such as oxides in the molten salt, which is beneficial to improve the heating quality of the workpiece. Compared with the traditional steel electrode, the graphite composite electrode has a life span of about 10 times that of the steel electrode, and the economic benefits are self-evident. We believe that with the development of industry, graphite composite electrodes will be more widely used.
To learn more about the product knowledge of graphite electrodes, please continue to pay attention to our website. If you need to buy high-quality graphite electrodes, please contact us. We will provide you with graphite electrode products that best suit your production needs according to your specific needs.

